WIND TURBINE DISPOSAL NIGHTMARE, SOLAR TOO


“The backlash was instant and uninformed,” Bratvold said. “Critics said they thought wind turbines were supposed to be good for the environment and how can it be sustainable if it ends up in a landfill?”
Clean energy’s dirty little secret on wind turbines
Built to withstand hurricane-force winds, turbine blades are not easily crushed, recycled or repurposed
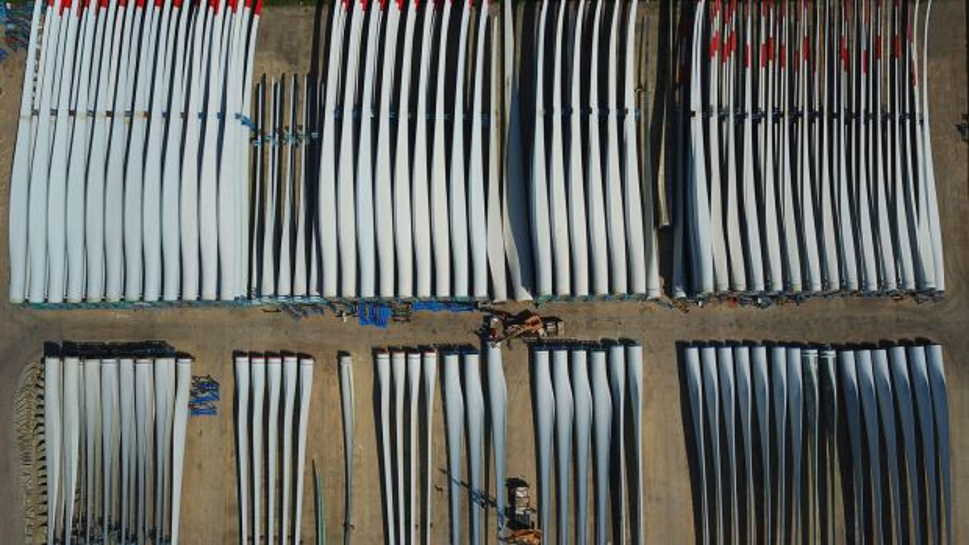
Tens of thousands of aging wind turbine blades are coming down and most have nowhere to go but landfills. Photograph: AFP via Getty Images

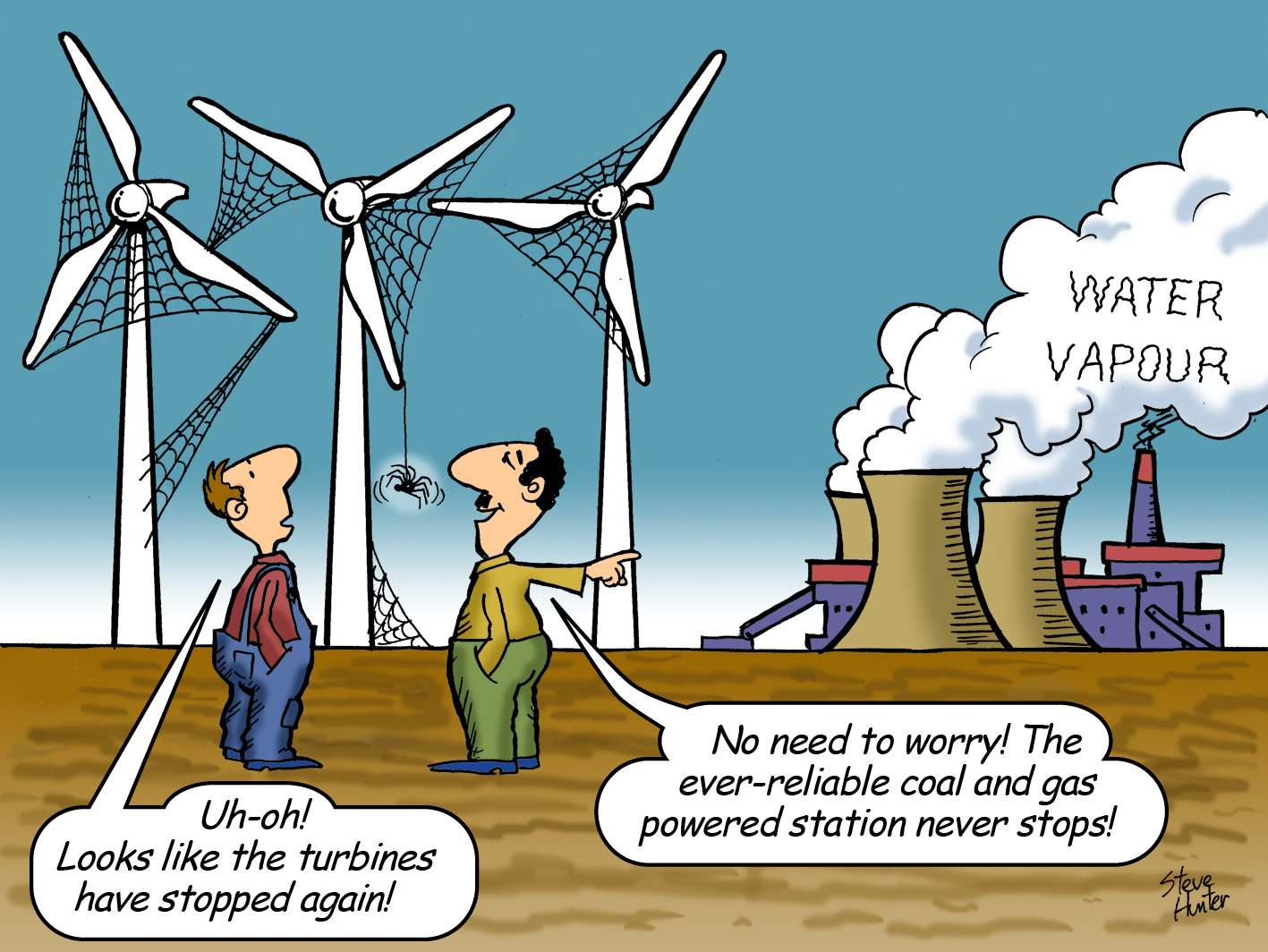
Wind turbine blades can be longer than a Boeing 747 wing, so at the end of their lifespan they cannot just be hauled away. First, you need to saw through the lissome fibreglass, using a diamond-encrusted industrial saw to create three pieces small enough to be strapped to a tractor trailer.
The municipal landfill in Casper, Wyoming, is the final resting place of 870 blades whose days making renewable energy have come to end. The severed fragments look like bleached whale bones nestled against one another.
“That’s the end of it for this winter,” said waste technician Michael Bratvold, watching a bulldozer bury them forever in sand. “We’ll get the rest when the weather breaks this spring.”
Tens of thousands of aging blades are coming down from steel towers around the world and most have nowhere to go but landfills. In the US alone, about 8,000 will be removed in each of the next four years. Europe, which has been dealing with the problem longer, has about 3,800 coming down annually through at least 2022, according to BloombergNEF. It’s going to get worse: Most were built more than a decade ago, when installations were less than a fifth of what they are now.
Urgent search
Built to withstand hurricane-force winds, the blades cannot easily be crushed, recycled or repurposed. That’s created an urgent search for alternatives in places that lack wide-open prairies. In the US, they go to the handful of landfills that accept them, in Lake Mills, Iowa; Sioux Falls, South Dakota; and Casper, where they will be interred in stacks that reach 30ft under.
“The wind turbine blade will be there, ultimately, forever,” said Bob Cappadona, chief operating officer for the North American unit of Paris-based VeoliaEnvironnement SA, which is searching for better ways to deal with the massive waste. “Most landfills are considered a dry tomb.
“The last thing we want to do is create even more environmental challenges.”
To prevent catastrophic climate change caused by burning fossil fuels, many governments and corporations have pledged to use only clean energy by 2050. Wind energy is one of the cheapest ways to reach that goal. (Editor’s note: absolutely nonsense: wind energy is not cheap, and not clean and not free.)
The electricity comes from turbines that spin generators. Modern models emerged after the 1973 Arab oil embargo, when shortages compelled western governments to find alternatives to fossil fuels. The first wind farm in the US was installed in New Hampshire in 1980, and California deployed thousands of turbines east of San Francisco across the AltamontPass.
The first models were expensive and inefficient, spinning fast and low. After 1992, when Congress passed a tax credit, manufacturers invested in taller and more powerful designs. Their steel tubes rose 260 feet and sported swooping fibreglass blades. A decade later, General Electricmade its 1.5 megawatt model – enough to supply 1,200 homes in a stiff breeze – an industry standard.
Difficult to dispose of
Wind power is carbon-free and about 85 per cent of turbine components, including steel, copper wire, electronics and gearing, can be recycled or reused. But the fibreglass blades remain difficult to dispose of. With some as long as a football field, big rigs can only carry one at a time, making transportation costs prohibitive for long-distance hauls. Scientists are trying to find better ways to separate resins from fibres or to give small chunks new life as pellets or boards. (Editor’s Note: we observe that in many if not most instances the steel from the towers cannot be recycled, as it has degraded and is not useable anymore.)
In the European Union, which strictly regulates material that can go into landfills, some blades are burned in kilns that create cement or in power plants. But their energy content is weak and uneven and the burning fibreglass emits pollutants.
In a pilot project last year, Veolia tried grinding them to dust, looking for chemicals to extract. “We came up with some crazy ideas,” Cappadona said. “We want to make it a sustainable business. There’s a lot of interest in this.”
One start-up, Global Fibreglass Solutions, developed a method to break down blades and press them into pellets and fibre boards to be used for flooring and walls. The company started producing samples at a plant in Sweetwater, Texas, near the continent’s largest concentration of wind farms. It plans another operation in Iowa.
“We can process 99.9 per cent of a blade and handle about 6,000 to 7,000 blades a year per plant,” said chief executive officer Don Lilly. The company has accumulated an inventory of about one year’s worth of blades ready to be chopped up and recycled as demand increases, he said. “When we start to sell to more builders, we can take in a lot more of them. We’re just gearing up.”
Safest and cheapest (Our note: they call them, “landfill safe.” You be the judge)
Until then, municipal and commercial dumps will take most of the waste, which the American Wind Energy Association in Washington says is safest and cheapest.
“Wind turbine blades at the end of their operational life are landfill-safe, unlike the waste from some other energy sources, and represent a small fraction of overall US municipal solid waste,” according to an emailed statement from the group. It pointed to an Electric Power Research Institute study that estimates all blade waste through 2050 would equal roughly .015 per cent of all the municipal solid waste going to landfills in 2015 alone.
In Iowa, Waste Management Inc “worked closely with renewable energy companies to come up with a solution for wind mill blade processing, recycling and disposal”, said Julie Ketchum, a spokeswoman. It disposes all the blades it receives, with as many as 10 trucks per day hauling them to the company’s Lake Mills landfill.
Back in Wyoming, in the shadow of a snow-capped mountain, lies Casper, where wind farms represent both the possibilities and pitfalls of the shift from fossil fuels. The boom-bust oil town was founded at the turn of the 19th century. On the south side, bars that double as liquor stores welcome cigarette smokers and day drinkers. Up a gentle northern slope, a shooting club boasts of cowboy-action pistol ranges. Down the road, the sprawling landfill bustles and a dozen wind turbines spin gently on the horizon. They tower over pumpjacks known as nodding donkeys that pull oil from wells.
“People around here don’t like change,” said Morgan Morsett, a bartender at Frosty’s Bar and Grill. “They see these wind turbines as something that’s hurting coal and oil.”
Cleaner to store
But the city gets $675,000 to house turbine blades indefinitely, which can help pay for playground improvements and other services. Landfill manager Cynthia Langston said the blades are much cleaner to store than discarded oil equipment and Casper is happy to take the thousand blades from three in-state wind farms owned by Berkshire Hathaway Inc’s PacifiCorp. Warren Buffett’s utility has been replacing the original blades and turbines with larger, more powerful models after a decade of operation.
While acknowledging that burying blades in perpetuity isn’t ideal, Bratvold, the special waste technician, was surprised by some of the negative reactions when a photo of some early deliveries went viral last summer. On social media, posters derided the inability to recycle something advertised as good for the planet, and offered suggestions of reusing them as links in a border wall or roofing for a homeless shelter.
“The backlash was instant and uninformed,” Bratvold said. “Critics said they thought wind turbines were supposed to be good for the environment and how can it be sustainable if it ends up in a landfill?”
“I think we’re doing the right thing.”
In the meantime, Bratvold and his co-workers have set aside about a half dozen blades and in coming months, they’ll experiment with methods to squeeze them into smaller footprints. They’ve tried bunkers, berms and even crushing them with the bulldozer, but the tracks kept slipping off the smooth blades. There’s little time to waste. Spring is coming, and when it does, the inexorable march of blades will resume. – Bloomberg


The last few years have seen growing concern over what happens to solar panels at the end of their life. Consider the following statements:
- The problem of solar panel disposal “will explode with full force in two or three decades and wreck the environment” because it “is a huge amount of waste and they are not easy to recycle.”
Today In: Industry
- “The reality is that there is a problem now, and it’s only going to get larger, expanding as rapidly as the PV industry expanded 10 years ago.”
- “Contrary to previous assumptions, pollutants such as lead or carcinogenic cadmium can be almost completely washed out of the fragments of solar modules over a period of several months, for example by rainwater.”
“We estimate there are 100,000 pounds of cadmium contained in the 1.8 million panels,” Sean Fogarty of the group told me. “Leaching from broken panels damaged during natural events — hail storms, tornadoes, hurricanes, earthquakes, etc. — and at decommissioning is a big concern.”
There is real-world precedent for this concern. A tornado in 2015 broke 200,000 solar modules at southern California solar farm Desert Sunlight.
“Any modules that were broken into small bits of glass had to be swept from the ground,” Mulvaney explained, “so lots of rocks and dirt got mixed in that would not work in recycling plants that are designed to take modules. These were the cadmium-based modules that failed [hazardous] waste tests, so were treated at a [hazardous] waste facility. But about 70 percent of the modules were actually sent to recycling, and the recycled metals are in new panels today.”
And when Hurricane Maria hit Puerto Rico last September, the nation’s second largest solar farm, responsible for 40 percent of the island’s solar energy, lost a majority of its panels.